CHIROPRACTIC CLINIC AND NATURAL HEALTH CENTRE • BACK PAIN? CONTACT US NOW FOR AN ASSESSMENT • ESTABLISHED 1984
HAYWARDS HEATH 01444 416911 info@freedom-healthcare.co.uk
Knees
I was proud of being promoted from the ski beginners to the not quite beginners ski group. However as I ploughed into another heavy turn on my first skiing trip off piste my ski tip caught in a patch or deep snow; my right leg twisted suddenly behind me causing a searing pain inside my knee as the rest of me tumbled ungraciously head over heels into a static heap. My French ski teacher and the rest of the class meanwhile disappeared into the distance none the wiser. Sadly that was the end of that ski trip, also the beginning of wearing a knee support for 12 months, and the beginning, for me, of taking a big interest in knees. X-rays revealed no damage but I had torn the soft tissue ligaments which take a long time to mend thoroughly.
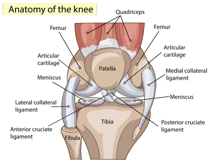
Anatomy or what makes up a knee:
The knee is the largest joint in the body. There are really three knee joints, one beneath the knee cap and the main joint which is divided into two, the medial and lateral joints between the long bone of the thigh, the femur, and the menisci, or cartilages, which are attached to the lower leg bone, the tibia. The menisci deepen the joint adding stability preventing side to side rocking within the joint. They are attached to the tibia around their outer edges, and are frequently torn. The knee joint is primarily a hinge, flexing and extending, but a small amount of rotation is also possible. Side to side movements are normally prevented by strong ligaments inside and outside the joint (the medial and lateral collateral ligaments) supported by muscles.
Knee injuries
A quarter of all women experience knee pain daily and women are about eight times more likely to suffer from a knee injury than men. The knees are susceptible to sports type injuries due to the relative instability of the joint which relies on the surrounding musculature for stability rather than its shape. The knee can absorb seven times the body weight when applied vertically- from the top down; but it is vulnerable to horizontal strains such as those which occur in tackles playing football. Actual lateral blows to the knee tend to tear the side ligaments particularly if the knee is straight/ extended at the time of impact. Some 50% of professional footballers have knee injuries during their career. The anterior cruciate ligament is more likely to be damaged by rapid directional changes while running.
Knee stability
Muscles used to be thought of as just the motors that moved the joint, but actually they provide much of the stability to the knee joint. Many knee problems stem from weakness in one or more of the knee muscles. For example when a muscle on the inside of the knee becomes weak the knee joint can bend abnormally inwards possibly leading to injury; it may cause the cartilage to catch or tear. In assessing the knees the surrounding muscles should be tested for strength and if weak treated appropriately to restore strength, this will often sort out a sore knee.
Treating the whole body
Knee pain is sometimes a secondary problem with the true cause found elsewhere in the body. We know the body works as a closed kinematic chain- this means like a wind up watch; you cannot move one piece of the watch without everything else being effected.
Pelvic balance is one of the most important factors is a balanced pelvis with properly functioning sacro-iliac joints and hips. These are routinely checked by chiropractors. The muscles that stabilise the knees are connected at their other end to the pelvis, so both need to be checked.
Feet and ankles
You can demonstrate the effect of the foot and ankle on the knees as follows. While standing roll in on your arches flattening your feet, and then roll out again; see the effect on your knees. As you roll in the knees come together putting pressure on the inside of the knees. If your feet are normally flat/pronated then shock will be transmitted from the floor through the feet to the knees with every step taken; orthotics or foot strengthening exercises may then be of benefit.
Muscle co-ordination
As one muscle contracts another must relax. When you bend your knee the hamstrings at the back of the knee contract while the quadriceps at the front relax/ pay out slack. In injuries this co-ordination may be lost.
Running
If you are fit running can provide a useful exercise but it puts three to seven times your body weight through each leg with each step, while walking is just one times. Why? Because you are moving faster. To avoid injuries to the knees it is better to avoid hard surfaces and instead choose surfaces that have shock absorbing qualities for the majority of your runs and be consistent with your route as changing surfaces can also lead to injuries. A web survey from fitsugar.com graded running surfaces from good to bad as follows: Grass 9.5,
Wood chips 9,
Dirt 8,
Cinder track 7.5
,Track 7,
Treadmill 6.5,
Asphalt 6,
Sand 4,
Snow 2.5,
Concrete 1. So maybe the local football field at least to start with whether you are walking or especially when running. Of course resilience should improve with training but don’t rush. I recommend my oldest ‘athletes for whom grass would be too uneven, get a trolley and walk around their local supermarket for a half hour daily! Nice smooth floors and something to hold on to is excellent for older people who like to exercise to stay fit. Don’t forget your loyalty card!
Non-Surgical Knee Surgery Alternatives Re-aligning the knee joint, balancing and strengthening the muscles; checking the feet for pronation/ flat feet and providing recommendations for their correction by manipulation or orthotics; checking the spine and pelvis for nerve supply to the leg muscles; good diet and advice on proper posture all can go a long way to correcting troublesome knee complaints If you are being offered surgery here are some further options you might like to try in addition to your chiropractic treatment as above:
Weight loss – most knee problems are made worse by being overweight. The best way to normalise weight is through having a permanently healthy diet that you enjoy, coupled with exercise rather than a series of fad diets. If you are overweight then avoid activities such as running and twisting which can aggravate the knee injury instead take up low impact exercise such as swimming the crawl or back stroke and Tai Chi. Specific exercises and physical therapy may help to improve strength and flexibility. Exercises may include strengthening exercises such as riding a stationary bike and weights particularly for the thigh muscle the quadriceps. Please see our personal trainer at the clinic for advice.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
Your GP can prescribe various drugs to reduce inflammation. Natural anti-inflammatories include omega 3 oils.
Glucosamine/Chondroitin There is a wealth of research into chondroitin and glucosamine over the last 20 years. Definitely worth discussing with your GP or health advisor to see if it can help you. It can thicken joint fluid and help repair cartilage. Glucosamine, chondroitin, MSM and collagen are all very similar.
Injection of joint fluid There is an injectable substance called synvisc or supartz which is a nature identical liquid. When injected it acts as a joint lubricant and can delay the need for joint replacement for months or years. Several of my patients have reported benefits although this is a last resort before replacement of a worn osteoarthritic knee. Several injections are usually needed from a consultant orthopaedic surgeon.
Summary Chiropractic treatment in combination with muscle and fascial release plus extremity mobilisation often alleviates knee pain by balancing muscle function and improving joint function. Exercise and nutrition can also play a big part.
